Page 3 of 8 |
Benefits
Converting the cores of Russia's three remaining operating production reactors offers significant benefits:
- International security will be enhanced by stopping production of weapons-grade plutonium at the reactors.
- The nuclear safety level and operating license will beapproved by the Russian regulatory agency, Gozatomnadzor (GAN).
- Some highly enriched uranium derived from dismantled weapons will be consumed in the converted reactors.
- The amount of spent fuel produced at the reactors will be reduced ten-fold.
- Spent fuel reprocessing will no longer be needed.
- The converted reactors will be less expensive to operate.
- Critically needed heat and electricity will continue to be provided to the surrounding regions in Siberia.
- Plutonium production will be halted while allowing time forthe Russians to build and bring alternative power sources online.
The Challenge of Core Conversion
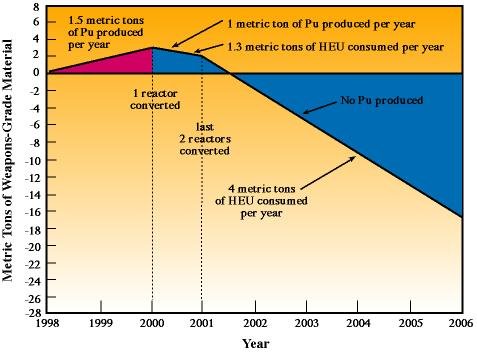
The Russian plutonium production reactors produce up to 1.5 metric tons of
weapons-grade plutonium per year. As 1960s-vintage reactors, they are in relatively good operating condition. However, there are safety concerns regarding their current mode of operation. Designed for weapons-grade plutonium production using low-burnup fuel, these reactors generate much more spent fuel than do normal power reactors. The challenge is to convert the reactors at Seversk and Zheleznogorsk quickly while continuing to provide the critically needed heat and electricity to the regions.
The converted reactors will consume a total of approximately 4 metric tons per year of highly enriched uranium that can be "mined" from dismantled nuclear weapons. In only about 2 years of operation, the new cores will consume the equivalent amount of weapons-grade materials accumulated in the four years estimated for completing core conversion, with a continuing consumption of approximately 4 metric tons per year.