![[Russia/America Flags]](inspmedia/cover.gif)
Fire Safety
Developing a Systematic Approach for Selecting Cost-Effective Upgrades
|
US Dept. of Energy Office of International Nuclear Safety and Cooperation 1000 Independence Ave S.W. Washington, DC 20585 (301) 903-0234 |
Nuclear power plants must be able to shut down safely in the event of fire. Current U.S. fire safety procedures for nuclear plants are the result of a 1975 fire at the Tennessee Valley Authority's Browns Ferry plant. The U.S. experience since 1975 has provided important insights to help improve fire safety at Soviet-designed nuclear power plants.
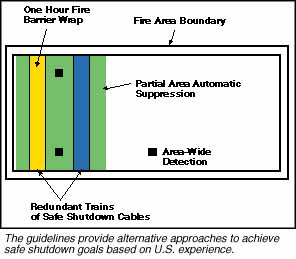
International standards call for redundant safety systems so that if a fire or explosion damages key equipment in one area of a plant, similar equipment in another area can be used to shut down safely and prevent core damage. Older models of RBMK and VVER plants either are not equipped with these redundant safety systems or do not provide adequate barriers between the systems. As a result, damage caused by fire in a single zone could lead to severe core damage and the release of radioactive materials. In cooperation with Ukraine and Russia, the U.S. Department of Energy has developed the Reactor Core Protection Evaluation Methodology for Fires at Soviet-Designed Nuclear Power Plants. The guidelines enable analysts to assess fire hazards and identify cost-effective changes in procedures and equipment, including the development of redundant safety systems. Pilot studies are underway at the Smolensk nuclear power plant in Russia and at the Zaporizhzhya nuclear power plant in Ukraine. As part of the studies, staff at the nuclear plants are working to:
As part of the pilot studies, recommended changes will be prioritized, so the most cost-effective measures can be implemented first. Implementing these recommended changes should reduce the risk of a large radioactive release in the event of a fire. Development of the guidelines was supported by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the U.S. commercial nuclear industry, with substantial input from international experts in the United Kingdom, Austria, Sweden, Finland, Germany, Belgium, Norway, and Italy. In addition to the studies, fire protection equipment and technology are being provided to help ensure safe shutdowns in fire emergencies. These include fire doors, penetration sealant and fire resistant cable coating, sprinkler systems, fire detection and alarm systems, fire resistant floor coating material, and structural steel coating material. |