 |
 LITHUANIA
LITHUANIA
Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
Country Profile SynopsisSize: 25,173 square miles (slightly larger than West Virginia)
Electricity Production1: 15.6 billion kWh (1998)
|
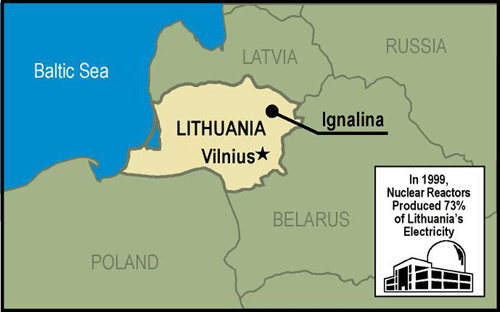
Lithuania's Nuclear Power Program
Since the breakup of the Soviet Union, Lithuania has relied increasingly on nuclear energy for electricity generation. Lithuania's Ignalina nuclear power plant has the world's two largest operating nuclear reactors-RBMK-1500s that together can produce approximately 2,760 MW of electricity. In 1999, the Ignalina plant provided 73 percent of Lithuania's electricity. The plant has the capacity to produce even more power, but safety concerns and public reaction to the Chornobyl accident prompted authorities to limit plant operation to lower power levels.
Lithuania has committed to shut down Unit 1 by the end of 2004.
Lithuania's Key Nuclear Organizations
- Lithuanian Nuclear Power Safety Inspectorate (VATESI) - Lithuanian nuclear regulatory authority.
- Ministry of Energy - agency responsible for nuclear power in Lithuania.
- Lithuania Energy Institute/Ignalina Safety Analysis Group - organization responsible for safety analyses for the Ignalina plant.
Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant

Plant Manager: Viktor N. Shevaldin
Chief Engineer: Genady Negrivoda
Utility: Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
Telephone No.: 370-66-28350
Fax: 370-66-29350
| Unit | Reactor Model | Net Output | Initial Start | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RBMK- 1500 | 1380 MWe | 10/1983 | Operating |
| 2 | RBMK- 1500 | 1380 MWe | 12/1986 | Operating |
Scope and Status of Activities
DOE's work at Ignalina nuclear power plant includes improving safety of day-to-day operations, upgrading critical safety systems, and transferring capability for performing reactor safety analyses. Projects include development of improved operating procedures and practices (1993-1998); development of a configuration management system (1995-997); provision of modern maintenance tools, equipment, and techniques (1995-1998); transfer of capabilities for performing plant safety analyses (1995-2005); and provision of up-to-date components for the plant's control-and-protection system (1995-2001).
Accomplishments
Management and Operational Safety- Operator exchanges that trained plant personnel to develop improved operating safety procedures and practices were completed.
- A complete set of management and operational control procedures that promote safety through improved operating practices was developed and implemented at the plant.
- A configuration management system was developed and implemented at the plant.
- The transfer of training technology and materials developed at the Balakovo Training Center to the Ignalina plant was completed and pilot courses were implemented for the Control Room Reactor Operator and Reactor Turbine Technician positions.
- State-of-the-art machines to cut pipes in vital safety systems precisely and prepare piping ends for welding were provided. Previously, workers cut pipes needing replacement by hand, which caused inaccurate welding and potential leakage.
- Ignalina maintenance technicians are using U.S.-supplied valve-seat resurfacing equipment to repair leaking valves at the plant. U.S. specialists provided associated training.
- Vibration monitoring and shaft alignment systems to detect and correct imbalances and shaft misalignment in rotating machinery were provided. U.S. specialists provided associated training.
- A U.S. expert is participating as a member of the Lithuania Nuclear Safety Commission. The commission meets several times a year to review operations at the Ignalina plant and advise the Lithuanian government.
- EOIs are complete at Ignalina, the technical justification documents are complete, and the EOIs have been validated against the technical justification documents. Training the operators on these new procedures is being conducted to support the implementation.
Engineering and Technology Upgrades
- The design, manufacture, and installation of an upgrade to the control-and-protection system for Unit 1 were completed. The upgraded system substantially reduces the risk of anticipated transients without scram, which were found to dominate the risk of operation of the unit. Equipment was also provided for the same upgrade to the control and protection system of Unit 2. The site acceptance test for the U.S.-supplied equipment was completed. The acceptance tests for the overall system, including software prepared by the plant, will be completed in 2000.
- Three hundred modern electronic instrumentation modules were provided to the plant to replace outdated, unreliable control modules.
- The preliminary design of a safety parameter display system was completed for Unit 2.
Plant Safety Evaluations
- Descriptions of RBMK reactor safety systems (including nominal plant parameters) were documented in the Ignalina Plant Parameter Source Book. The source book contains the most definitive data available for the RBMK-1500 reactor safety systems and has received broad international distribution.
- Software, hardware, and training on the use and application of probabilistic risk assessment software were transferred to the Ignalina plant.
- An RBMK thermal-hydraulic safety analysis model was developed for the plant.
- An interactive nuclear plant analyzer was developed to perform safety evaluations and analyses using RELAP5 thermal-hydraulic computer models of the Ignalina RBMK reactor.
- A pressure tube gap closure thermal-hydraulic analysis was completed. Detailed stress analysis of the pressure tube and associated hardware was completed.
- Structural mechanics codes were provided to analyze the consequences of various accident scenarios. For example, the consequences of a pipe rupture at the plant's group distribution header are being studied.
| | Contents | Foreword | Program Overview | Armenia | Bulgaria | Czech Republic | Hungary | Kazakhstan | Lithuania | Russia | Slovakia | Ukraine | Appendix A | Appendix B | Appendix C | Contacts | |