 |
 ARMENIA
ARMENIA
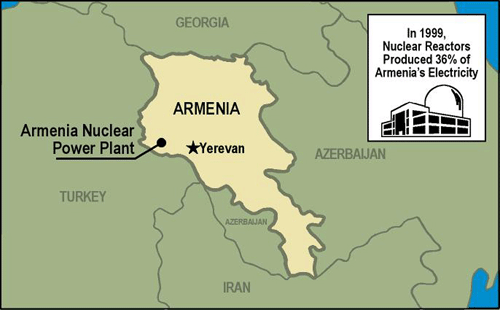
Armenia Nuclear Power Plant
Country ProfileSize: 11,500 square miles (slightly smaller than Maryland)Population1: 3.4 million (1999 est.) Gross Domestic Product1: $9.2 billion (1998 est.) (purchasing power parity) Gross Domestic Product per Capita: $2,700 (1998 est.) Electricity Production1: 5.7 billion kWh (1998) |
Armenia's Nuclear Power Program
The Armenia nuclear power plant is located at Medzamor. The plant consists of two modified VVER?440/230s. The units have been modified with seismic upgrades and are sometimes referred to as Model V270s. Seismic reinforcements have been made to the reactor building and structures, electrical cabinets, and cooling towers. In addition, the Model V270s have primary coolant pumps with longer coast-down time, an additional emergency feedwater system, and a backup residual heat removal system.
Both units were shut down in early 1989 following an earthquake. In 1993, the government decided to restart the plant and, in late 1995, Unit 2 was placed back on line. Unit 2 was selected for restart because it is the newer of the two units. Armenian officials have said Unit 1 will not be restarted.
Armenia's first priority is to ensure the safe operation of Unit 2 and bring it closer to international safety practices. In 1999, Unit 2 supplied 36 percent of the country's electricity.
In 1995, the Armenian government documented its energy program to the year 2005, which included a two-stage plan for nuclear energy development. The first stage entails operating the plant until 2005, and the second stage calls for bringing a new nuclear power plant on line between 2005 and 2010. The Armenian government has committed to the permanent shutdown of Unit 2 when a new nuclear power plant is brought on line. The government's long-term program calls for nuclear energy to provide 38 percent of the country's electricity.
Armenia's Key Nuclear Organizations
Ministry of Energy - agency responsible for Armenian Nuclear Power Plant.
Armenian Nuclear Regulatory Authority - Armenia's nuclear regulatory body formed in 1994.
Armenia Nuclear Power Plant

Plant Manager: Souren G. Azatian
Chief Engineer: Gagik Markosyan
Utility: Armenian Nuclear Power Plant Company
Telephone No.: 374-259-2377
Fax: 374-215-1860
| Unit | Reactor Model | Net Output | Initial Operation | Current Status |
| 1 | VVER-440, Model 230 | 410 MWe | 12/1976 | Shut Down 1989 |
| 2 | VVER-440, Model 230 | 410 MWe | 12/1979 | Operating |
Scope and Status of Activities
DOE's cooperative efforts at Unit 2, the only operating reactor at Armenia nuclear power plant, have focused primarily on fire safety improvements and safety systems upgrades-two of the most critical safety deficiencies at the plant. Projects associated with these efforts were initiated in late 1996 and are scheduled to be completed during 2001. Projects to address needs in operational safety, safety maintenance, and safety analysis capability were initiated in 1998. Their completion is scheduled for 2003. In 1999, a decommissioning planning project was initiated. The plant is scheduled for shutdown in 2004. As shutdown approaches, the support for decommissioning activities will increase. The U.S. Agency for International Development is providing the funding for the safety work in Armenia.
Accomplishments
Management and Operational Safety
- A U.S. expert is serving as a member on the Armenian President's Nuclear Safety Advisory Committee that meets several times a year to review safety at the plant and advise the Armenian president.
- Training courses for the Control Room Reactor Operator, Radiation Protection Technician, and Reactor Equipment Maintenance Shop Foreman positions were developed and implemented. A workshop to improve management and supervisory skills was also completed.
- Ultrasonic testing, vibration monitoring, motor shaft alignment, thermographic and valve repair equipment was delivered to the plant and associated training was provided.
- A draft preliminary decommissioning plan was completed and is under review. The final version will be issued in 2000.
Engineering and Technology Upgrades
- As part of the fire-safety upgrade project, the United States supplied fire-resistant floor-coating material to replace the flammable plastic floor covering at the plant. The coating was applied to all of the critical floor area in the reactor building (12,000 m2). Installation was conducted by U.S.-trained plant personnel. A fire-detection and alarm system was provided to the plant and installation was completed. The system will be programmed and commissioned before the end of 2000. One hundred and forty fire doors have been manufactured and installed at the plant. Double fire doors (20), which failed the fire test in Russia, were redesigned and will be installed by the end of 2000. A new air-charging station for self-contained breathing apparatus was provided to the fire department.
- The United States provided equipment to complete a seismic-resistant, spray pond cooling system to remove safety system heat loads. Construction of the three ponds, two pump stations, and concrete tunnels for electric power lines was completed. The pumps that provide the motive force for the system were procured, delivered, and installed. Tie-in to the plant, integral testing, and commissioning of the system will occur during the autumn outage in 2000.
- The United States provided a diesel-driven emergency water pumping system to serve as a backup to the emergency feedwater system. The emergency feedwater system will be installed while the plant is at power, prior to the spring outage in 2001.
- Seven replacement main steam-isolation valves were manufactured and delivered to the plant and installed. The actuators for the valves will be installed and the system tested and commissioned for operation during the autumn outage in 2000.
Plant Safety Evaluations
- Training was provided to the plant for the seismic evalu-
ation of plant safety equipment. A seismic inspection of the plant was conducted in September 2000 that identified safety equipment requiring corrective action or further structural analysis to determine its seismic reliability. The walkdowns involved international seismic safety experts, who examined the seismic robustness of critical plant safe-shutdown equipment and trained plant personnel in the identification of seismic deficiencies.
- A plan was developed and approved that maps out DOE projects to support the development of safety analysis capability in Armenia. As a first step, training was provided to the plant and Armatom, the Armenian technical support organization, in the use of the RELAP5 thermohydraulic code that will be used for safety assessments of plant operations.
- The draft decommissioning plan for the plant was completed and is under
review.
| | Contents | Foreword | Program Overview | Armenia | Bulgaria | Czech Republic | Hungary | Kazakhstan | Lithuania | Russia | Slovakia | Ukraine | Appendix A | Appendix B | Appendix C | Contacts | |