Improving the Safety of Soviet-Designed Nuclear Power Plants--Overview
Important Note: This website contains historical data from the INSP project. As of 2004 the site is no longer maintained and certain sections do not work correctly.
 |
| Summary |
| Introduction | ||
| Historical Issues and Reactor Types | ||
| Reducing Risks | ||
| Key Accomplishments | ||
| Performace Measurement and Future Directions | ||
| Timeline (1986-1999) | ||
| Contacts |
The U.S. Department of Energy manages a comprehensive collaborative effort to improve nuclear safety at Soviet-designed nuclear power plants in nine partnering countries. In addition to these nine host countries, the G-7 nations and many international organizations collaborate on this effort.
Improve Safety and Reduce Risks By
- improving physical operating conditions
- installing safety equipment
- developing improved safety procedures
- establishing regional centers for training reactor personnel
- installing simulators for training control room operators
- conducting in-depth safety assessments
- developing institutional and regulatory frameworks
- addressing the extraordinary problems at Chornobyl.
Benefits
- Reduces the likelihood of a nuclear accident.
- Protects Europe's public, economic and environmental health and the health of U.S. citizens in Europe.
- Promotes a stable climate for international investments in countries with Soviet-designed reactors.

Vent stack (right) identifies the Kola nuclear power plant on the Kola peninsula in northwestern Russia.
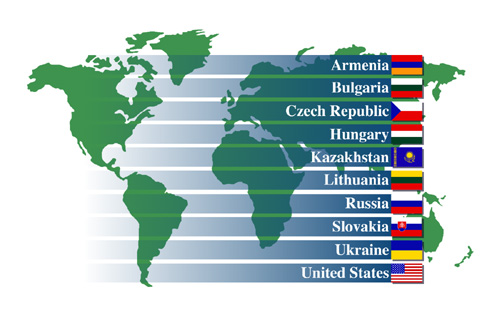
Host Countries and Nuclear Power PlantsArmenia -- Armenia plant, one VVER-440/230 reactor Bulgaria -- Kozloduy plant, four VVER-440/230, two VVER-1000 reactors Czech Republic -- Dukovany plant, four VVER-440/213 reactors Hungary -- Paks plant, four VVER-440/213 reactors Kazakhstan -- Aktau plant, one BN-350 reactor Lithuania -- Ignalina plant, two RMBK-1500 reactors Russia -- Balakovo, Bilibino, Beloyarsk, Kalinin, Kola, Kursk, Leningrad, Novovoronezh, and Smolensk plants
Slovakia -- Bohunice plant, two VVER-440/230, two VVER-440/213 reactors Ukraine -- Chornobyl, Khmelnytskyy, Rivne, South Ukraine, and Zaporizhzhya plants
Reactor Types
|
| Page 1 of 8 |
 |